Spring AOP 实现之注解配置
1. 前言
大家好,本小节,我们学习 Spring 框架 AOP 的另外一种实现形式 —— 注解模式。在上小节中我们使用 XML 配置文件的方式已经体验过了 Spring 的 AOP。
那么对于注解来实现,大致步骤思路相同,只需要将 xml 配置的 AOP 替换成注解即可。如何实现呢? ok,大家随我来进入本小节课程的学习。
2. 实例演示
2.1 工程搭建介绍
数据库表结构:
建表 SQL 语句如下:
CREATE TABLE `account` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL auto\_increment COMMENT 'id',
`accountNum` varchar(20) default NULL COMMENT '账号',
`money` int(8) default NULL COMMENT '余额',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO\_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
工程代码介绍:
- 实体类: 跟数据库表对应的 Java 类 Account ;
- 操作实体类: Dao 和 Dao 的接口实现类 ;
- 调用持久层的业务类: Service 和 Service 的实现类 ;
- 事务管理器类: TransactionManager 提供事务的一系列操作 ;
- 测试代码类: 初始化 Spring 调用类中的方法测试 。
使用注解介绍:
- @Aspect: 此注解用于表明某个类为切面类,而切面类的作用我们之前也解释过,用于整合切入点和通知;
- @Pointcut: 此注解用于声明一个切入点,表明哪些类的哪些方法需要被增强;
- @Before: 此注解一看就明白,表示一个前置通知。即在业务方法执行之前做的事情;
- @AfterReturning: 此注解表示一个后置通知。即在业务方法执行之后做的事情;
- @After:此注解一个最终通知。即在业务方法执行之前做的事情;
- @AfterThrowing:此注解表示一个异常通知。即在业务代码执行过程中出现异常做的事情。
2.2 代码实现
1. 创建 maven 工程:

pom 文件的 jar 包坐标如下:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-dbutils</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbutils</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>c3p0</groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0</artifactId>
<version>0.9.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.8.7</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2. 连接数据库的工具类:
@Component
public class ConnectionUtils {
private ThreadLocal<Connection> tl = new ThreadLocal<Connection>();
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
/\*\*
\* 获取当前线程上的连接
\* @return
\*/
public Connection getThreadConnection() {
try{
//1.先从ThreadLocal上获取
Connection conn = tl.get();
//2.判断当前线程上是否有连接
if (conn == null) {
//3.从数据源中获取一个连接,并且存入ThreadLocal中
conn = dataSource.getConnection();
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
tl.set(conn);
}
//4.返回当前线程上的连接
return conn;
}catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/\*\*
\* 把连接和线程解绑
\*/
public void removeConnection(){
tl.remove();
}
}
3. 实体类 Account:
public class Account implements Serializable {
//数据id
private Integer id;
//账号编码
private String accountNum;
//账号金额
private Float money;
//省略get 和set 方法
}
4. 持久层 dao 和 dao 的 实现类:
//dao的接口
public interface IAccountDao {
/\*\*
\* 更新
\* @param account
\*/
void updateAccount(Account account);
/\*\*
\* 根据编号查询账户
\*/
Account findAccountByNum(String accountNum);
}
//dao的实现类
@Repository
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
//dbutil的查询工具类
@Autowired
private QueryRunner runner;
//连接的工具类
@Autowired
private ConnectionUtils connectionUtils;
public void setRunner(QueryRunner runner) {
this.runner = runner;
}
public void setConnectionUtils(ConnectionUtils connectionUtils) {
this.connectionUtils = connectionUtils;
}
//修改账号
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
try{
runner.update(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),"update account set accountNum=?,money=? where id=?",account.getAccountNum(),account.getMoney(),account.getId());
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//根据账号查询
public Account findAccountByNum(String accountNum) {
try{
List<Account> accounts = runner.query(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),"select \* from account where accountNum = ? ",new BeanListHandler<Account>(Account.class),accountNum);
if(accounts == null || accounts.size() == 0){
return null;
}
if(accounts.size() > 1){
throw new RuntimeException("结果集不唯一,数据有问题");
}
return accounts.get(0);
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
代码解释: AccountDaoImpl 类上面的注解 @Repository 表示使用注解实例化此类,并交给 Spring 的容器管理。
5. 业务类 Service 和 Service 的实现类:
//业务接口
public interface IAccountService {
/\*\*
\* 转账
\* @param sourceAccount 转出账户名称
\* @param targetAccount 转入账户名称
\* @param money 转账金额
\*/
void transfer(String sourceAccount, String targetAccount, Integer money);
}
//业务实现类
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
@Autowired
private IAccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(IAccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
public void transfer(String sourceAccount, String targetAccount, Integer money) {
Account source = accountDao.findAccountByNum(sourceAccount);
Account target = accountDao.findAccountByNum(targetAccount);
source.setMoney(source.getMoney()-money);
target.setMoney(target.getMoney()+money);
accountDao.updateAccount(source);
accountDao.updateAccount(target);
System.out.println("转账完毕");
}
}
代码解释:AccountServiceImpl 类上面的注解 @Service 表示使用注解实例化此类,并交给 Spring 的容器管理。
6. 事务管理器类
@Component
@Aspect
public class TransactionManager {
@Autowired
private ConnectionUtils connectionUtils;
public void setConnectionUtils(ConnectionUtils connectionUtils) {
this.connectionUtils = connectionUtils;
}
@Pointcut("execution(\* com.offcn.service.impl.\*.\*(..))")
private void pt1() {}
/\*\*
\* 开启事务
\*/
@Before("pt1()")
public void beginTransaction(){
try {
System.out.println("开启事务");
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().setAutoCommit(false);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/\*\*
\* 提交事务
\*/
@AfterReturning("pt1()")
public void commit(){
try {
System.out.println("提交事务");
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().commit();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/\*\*
\* 回滚事务
\*/
@AfterThrowing("pt1()")
public void rollback(){
try {
System.out.println("回滚事务");
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().rollback();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/\*\*
\* 释放连接
\*/
@After("pt1()")
public void release(){
try {
System.out.println("释放连接");
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().close();//还回连接池中
connectionUtils.removeConnection();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
代码解释:
此类通过注解 @Componet 实例化,并且交由 Spring 容器管理,@Aspect 表明它是一个切面类。而下面的注解 @Pointcut 和其余的方法上的各个通知注解,在上面也已经介绍过,这里不做赘述了。
主要专注点在于每个注解的通知方法内部引入切入点的表达式方式。
7. 配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--配置QueryRunner-->
<bean id="runner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner" scope="prototype"></bean>
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<!--连接数据库的必备信息-->
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/transmoney"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 注解扫描工程下的包路径-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.offcn"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 注解代理模式 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
</beans>
配置文件说明:
- dataSource: 采用 c3p0 数据源,大家一定要注意数据库的名称与账号名和密码;
- queryRunner: dbutils 第三方框架提供用于执行 sql 语句,操作数据库的一个工具类;
- context:component-scan: 此注解表示注解方式初始化容器扫描的包路径;
- aop:aspectj-autoproxy: 此注解表示开启代理模式
8. 测试类代码
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class AccountServiceTest {
@Autowired
private IAccountService accountService;
@Test
public void testTransfer(){
accountService.transfer("622200009999","622200001111",100);
}
}
测试结果:
执行代码后结果:
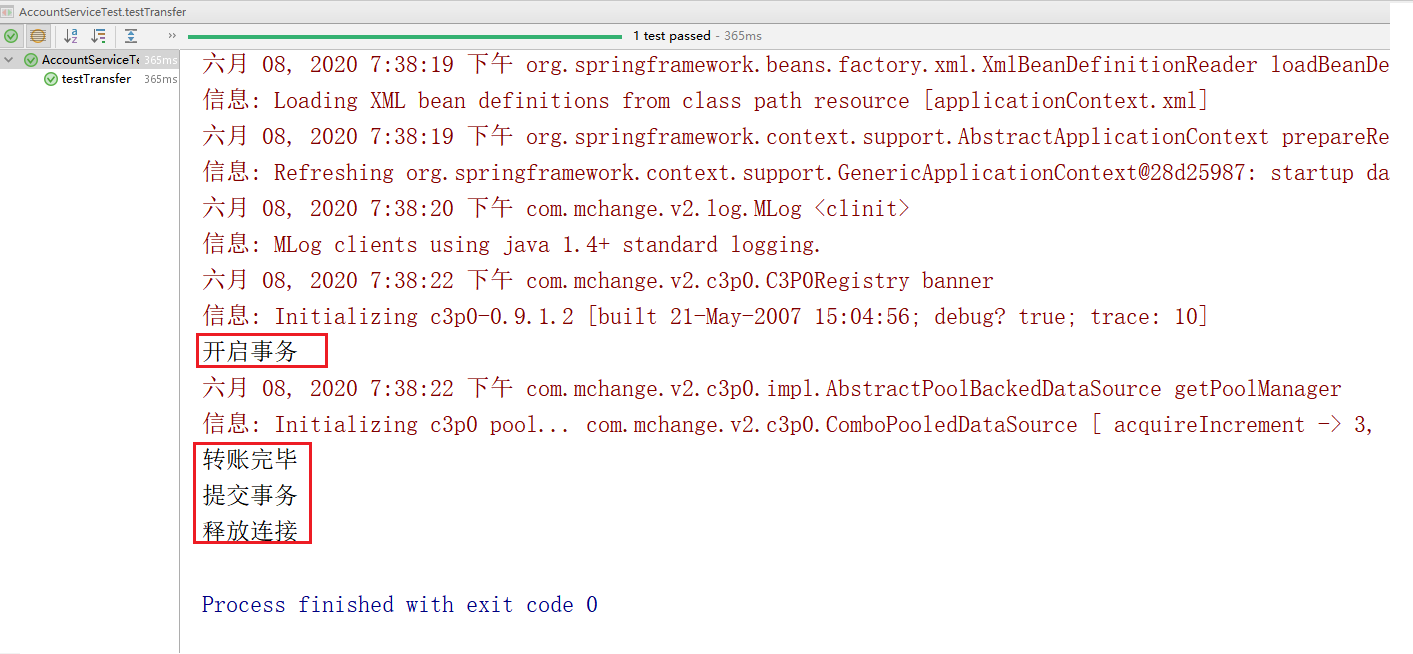
可以看到,我们通过注解方式配置 Spring 的 AOP 相关配置,同样实现了对于数据的操作。
3. 小结
本小节学习了 Spring 中 AOP 的注解实现,那么哪些要求大家掌握的呢?
- AOP 使用的相关注解有哪些;
- AOP 每种注解的使用方式以及作用;
- AOP 切入点的表达式写法。